In this Article
The Northern Melbourne Smart Cities Network (NMSCN), enabling data to drive change project, project stands as a testament to the transformative power of smart city technology. This ambitious initiative, the largest of its kind in Australia, is a collaborative effort to harness the potential of IoT (Internet of Things) for improved urban management and service delivery. Funded through a $1.5M federal grant from the smart cities and suburbs program, the project has brought together multiple councils, industry partners, and academic institutions, all working towards a common goal: to make Northern Melbourne a leader in smart city innovations.
Project Overview
The NMSCN project was initiated to address the growing challenges of urbanisation, including traffic congestion, resource management, and environmental sustainability. By deploying an extensive network of IoT sensors and leveraging advanced data analytics, the project aims to enhance operational efficiency, provide real-time data insights, and support strategic decision-making across five local councils: City of Whittlesea, Banyule City Council, Moreland City Council, Mitchell Shire Council, and Nillumbik Shire Council.
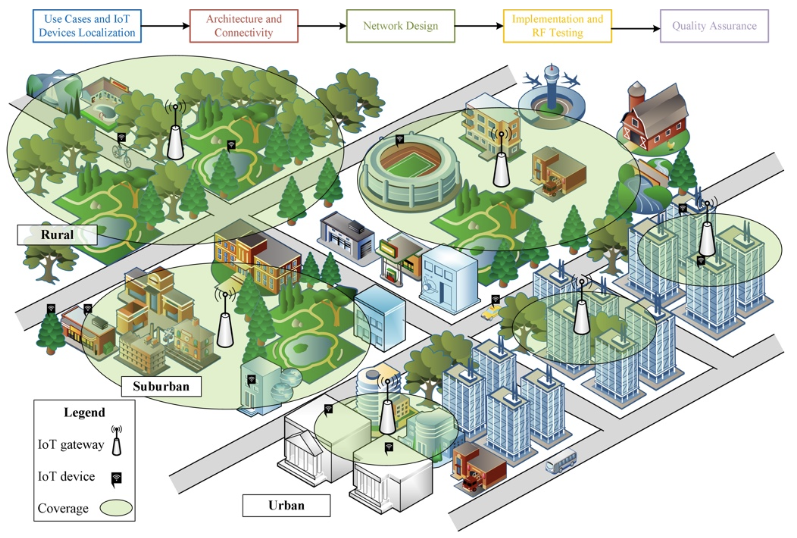
Objectives and Use Cases
The primary objectives of the NMSCN project include:
- Enhanced Service Delivery: Improve the efficiency and responsiveness of municipal services through real-time data collection and analysis.
- Environmental Monitoring: Track environmental parameters such as air quality, water levels, and waste management to support sustainability initiatives.
- Community Engagement: Foster a transparent and collaborative relationship between the councils and the community by providing open access to data and encouraging citizen participation.
Key use cases implemented under the NMSCN project include:
- Smart Waste Management: Sensors in public bins monitor fill levels, enabling optimized waste collection routes and reducing overflow incidents.
- Water Level Monitoring: Sensors in creeks and reservoirs provide real-time data on water levels, helping to prevent flooding and manage water resources effectively.
- Environmental Sensing: Air quality sensors measure pollutants, temperature, and humidity, providing valuable data for public health and policy-making.
- Occupancy Estimation: Sensors in public spaces such as parks and shopping strips count foot traffic, assisting in urban planning and resource allocation.
- Asset Tracking: GPS-enabled devices on council vehicles and equipment improve asset management and operational efficiency.
Collaboration and Partnerships
The success of the NMSCN project is largely attributed to the robust collaboration between various stakeholders, including local councils, universities, and industry partners. Each entity brought unique expertise and resources to the table, facilitating a comprehensive and well-rounded approach to the project.
Local Councils
The five participating councils played a crucial role in defining the project’s scope, identifying key areas of need, and facilitating on-ground implementation. Their active involvement ensured that the solutions developed were tailored to address specific local challenges.
Academic Institutions
RMIT University and La Trobe University were instrumental in providing research support and technical expertise. RMIT University led the network design, testing, and quality assurance processes, while La Trobe University focused on data analytics and visualization. Their contributions ensured that the project was grounded in cutting-edge research and best practices.
Industry Partners
Minnovation Technologies, the industry partner, was responsible for the supply and installation of IoT sensors and gateways. Their role extended to providing ongoing maintenance and support, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the network infrastructure in the Northern Melbourne Smart Cities Network.
Implementation Strategy
The implementation of the NMSCN project followed a meticulously planned approach, involving several key phases:
1. Network Design
The design phase involved selecting optimal locations for IoT sensors and gateways. This was achieved through a combination of site surveys, RF ray tracing simulations, and coverage mapping. The goal was to ensure maximum coverage and data accuracy while minimising costs.
2. Infrastructure Deployment
The deployment phase focused on the physical installation of the network components. This included mounting gateways on rooftops and placing sensors in strategic locations. The process was carried out with minimal disruption to public spaces, adhering to safety and regulatory standards.
3. Data Integration
Once the sensors were operational, the next step was integrating the collected data into a centralised platform. Minnovation’s AlphaX Cloud Smart City Platform was chosen for its robust cloud computing capabilities, providing a secure and scalable environment for data storage and processing.
Through an additional partnership with Microsoft, The data was then made accessible through Power BI dashboards, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis.
4. Testing and Optimisation
Extensive testing was conducted to validate the network performance. This included field measurements using packet testers to assess signal strength and data transmission reliability. The results were used to fine-tune the network configuration and address any coverage gaps or interference issues.
5. Quality Assurance
Quality assurance was a critical component of the project, ensuring that the installation met all technical specifications and performance benchmarks. Regular inspections and maintenance checks were conducted to maintain the integrity of the network.
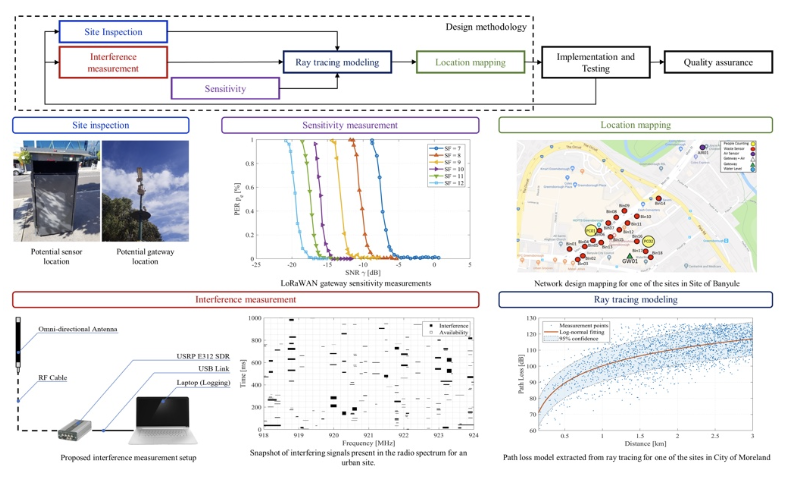
Key Challenges and Solutions
Despite the project’s success, several challenges were encountered and addressed through innovative solutions:
1. Installation Constraints
Installing sensors and gateways in urban environments posed logistical challenges, including access restrictions and interference from buildings and foliage. These were mitigated through careful planning and the use of advanced RF simulation tools to identify optimal installation sites.
2. Data Management
Handling large volumes of data from diverse sources required a robust data management strategy. Minnovation’s AlphaX cloud services provided the necessary scalability and security, while Microsoft Power BI facilitated intuitive data visualisation and reporting.
3. Community Engagement
Ensuring community buy-in and participation was essential for the project’s long-term success. This was achieved through public workshops, transparent communication, and providing open access to the data collected by the network.
4. Covid Outbreak
Despite the unprecedented challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, the Northern Melbourne Smart Cities Network project was successfully completed, showcasing the resilience and adaptability of the teams involved. This accomplishment highlights the collaborative efforts and innovative strategies employed to overcome logistical and operational hurdles during the outbreak, ensuring the project’s objectives were met on time.
Impact and Outcomes
The NMSCN project has had a profound impact on the participating councils and the broader community. Key outcomes include:
- Improved Service Delivery: Real-time data has enabled more efficient waste collection, water management, and maintenance operations, leading to cost savings and enhanced service quality.
- Environmental Benefits: Continuous monitoring of environmental parameters has informed policy decisions and public awareness campaigns, contributing to improved air quality and water management.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: The availability of detailed data analytics has supported evidence-based decision-making, helping councils to prioritize resources and plan for future needs effectively.
- Community Engagement: The project has fostered a culture of transparency and collaboration, empowering citizens to engage with their local government and participate in smart city initiatives.
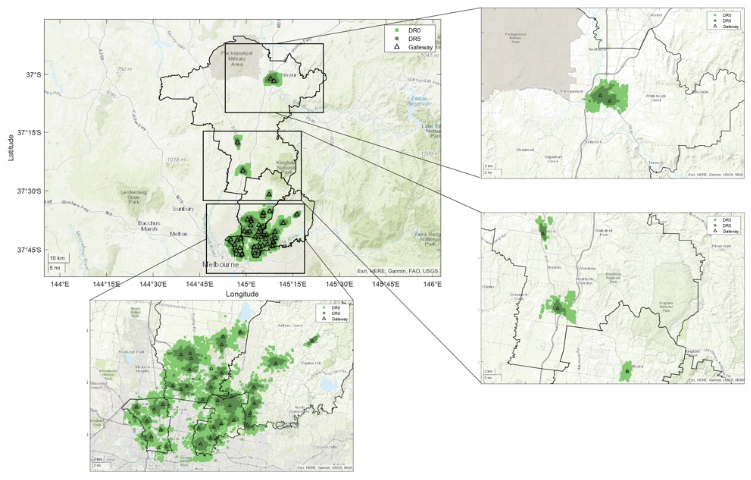
Awards and Recognition
The NMSCN project has received significant recognition for its innovative approach and successful implementation. It has been awarded two prestigious industry awards:
- MAV Technology Awards for Excellence 2020: Recognising the project’s contribution to technological innovation in local government. MAV Technology Awards.
- IoT Alliance Australia (IoTAA) Smart Cities Award 2020: Highlighting the project’s impact on smart city development and IoT integration. IoT Hub Awards.
Future Prospects
Building on the success of the initial deployment, the NMSCN project is poised for further expansion and innovation. Future plans include:
- Network Expansion: Extending the network to cover additional areas and incorporate more sensors, further enhancing data collection and service delivery.
- Advanced Analytics: Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to gain deeper insights from the collected data and predict future trends.
- Cross-Council Collaboration: Strengthening partnerships between councils and other stakeholders to share knowledge, resources, and best practices.
Conclusion
The Northern Melbourne Smart Cities Network project exemplifies the potential of smart city technology to transform urban management and service delivery. Through collaborative efforts, innovative solutions, and a commitment to excellence, the project has set a benchmark for future smart city initiatives. The lessons learned and successes achieved serve as a blueprint for other regions seeking to harness the power of IoT for the benefit of their communities.
As smart cities continue to evolve, projects like the NMSCN will play a crucial role in shaping the future of urban living, making cities more efficient, sustainable, and responsive to the needs of their residents. The journey of the NMSCN project is a testament to what can be achieved when vision, technology, and collaboration come together in pursuit of a common goal.
Related Blog Posts
How Smart Cities Connect: Getting Started with Edge AI and IoT Technology
How to Get Started with Edge AI and IoT Technologies in Smart Cities: Overcoming Integration Challenges In recent years, the concept of smart cities has evolved from a futuristic Read More
5 Step Strategy: Ensuring Security and Privacy in 15-Minute Smart Cities
Introduction Ensuring security and privacy in 15-minute smart cities is a critical challenge as urban areas become increasingly connected through IoT and edge AI technologies. These cities aim to Read More
What is a smart city and the challenge of legacy systems
How to Get Started with Integrating Legacy Systems in Smart Cities Smart cities are transforming urban landscapes by leveraging technology to improve the quality of life for residents. However, Read More




